In the digital landscape, the SaaS market resembles a vast interconnected network of diverse platforms collaborating to create effective ecosystems. This concept is precisely what interoperability entails: the capacity of solutions to communicate and utilize information interchangeably.
The ease with which data are exchanged brings numerous benefits to the end-users and companies that wish to expand their knowledge base for better decision-making processes.
This article will explore the importance of interoperability for the digital market and the benefits it brings to companies and customers.
1. What is interoperability?
Interoperability, to put it simply, is the ability of solutions to communicate seamlessly through established connections. No manual intervention from the user is required for it. Interoperable components encompass functions such as data access, data transmission, and cross-organizational collaboration, regardless of their developer or source.
How is it established? Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) provide a set of rules and protocols that allow different software applications to interact with each other. By exposing specific functions and data through APIs, systems can communicate and exchange information in a standardized way.
Interoperability vs compatibility
At first glance, interoperability and compatibility are often confused.
Compatibility also implies the interaction of two or more applications, but in this case, they are within a shared environment. These applications perform their tasks independently without causing any disruption or interference to other applications or systems. They do not need to communicate with each other.
Interoperability, on the other hand, requires the interaction of the apps that are in dissimilar environments. Data exchange and its treatment are the primary characteristics.
2. Horizontal vs vertical interoperability
When we refer to horizontal or vertical interoperability, we mean the type of relationship that interoperable applications have with each other.
Vertical interoperability is when there is the exchange and integration of data or functionalities between different levels or layers of a specific industry or domain.
For example, ViiBE’s video assistance tool is integrated with Zendesk. An expert can trigger a video call directly from the Zendesk ticket and all the shared media and video recordings of the session will be stored in that exact same ticket.
Horizontal interoperability is when the exchange happens at the same level. For example, when you receive an Outlook email on your Gmail instance or the merger of Facebook and WhatsApp.
In this article, we will focus on vertical interoperability to illustrate how different tools in your product suite can be connected and how you can use the generated data to understand your customers better, evaluate to what extent your product serves customer needs, and as a result, maintain the growth of your business.
3. Why does the digital market need interoperability?
With technological advancements, the landscape of digital solutions has gone through a major transformation and now resembles a spiderweb of various tools that serve different market needs. Globalization changed the rules of the game allowing everyone to become a member of the global market and diminishing the hierarchical organization (when a few big actors dominated the market).
Nowadays if a solution is not interoperable, it risks losing a major market share and being replaced by another player that is more adaptive and agile. Therefore, companies are looking for ways to clearly communicate the value they deliver and yet form clusters with relatable solutions that would help them reach a wider audience.
This process brings significant advantages to digital solutions and their customers.
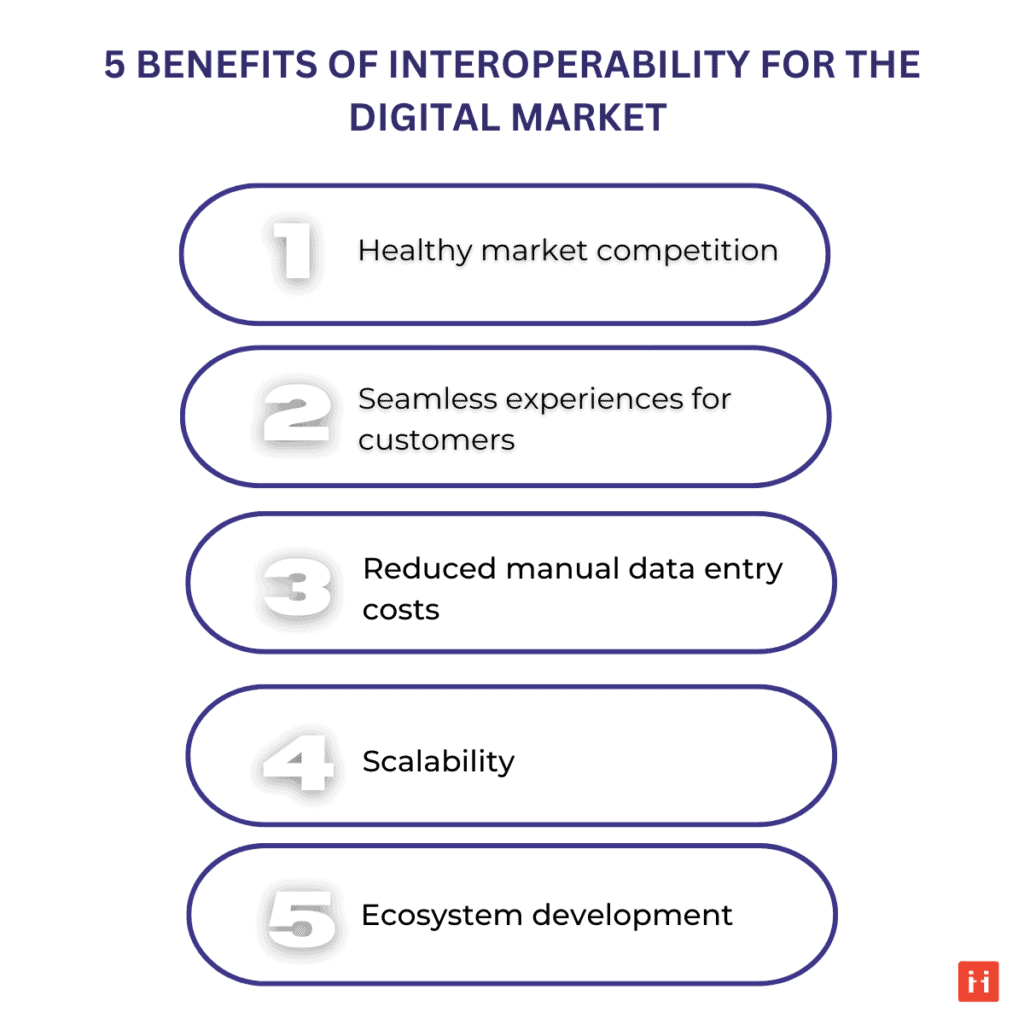
3.1. Interoperability promotes healthy market competition
Competition is a founding block of the free market economy. When customers have a variety of solutions, it stimulates companies to create better products because once the company does not satisfy the need, the customer quickly switches to the new one.
When numerous solutions are available, customers avoid “vendor lock-in” when they have to rely only on one provider for a specific service. In the case of a monopoly, there is a risk of data silos, and thanks to interoperability, it can be avoided.
Many digital systems, applications, and databases have been developed independently over time. Interoperability enables the integration of these existing systems, allowing users to elicit the maximum value from each one.
3.2. Customers benefit from seamless experiences
Seamless interaction between digital services that does not make users change their user habits is one of the biggest advantages of interoperability.
For example, ViBE’s video assistance tool is integrated with Praxedo’s field service management solution. A technical support expert can trigger a video call directly from Praxedo’s interface. He/she sends a field technician an sms to join a video recording interface, where both interlocutors can see the encountered problem, use collaborative tools, and exchange media files.
All the files will be saved in one place for the experts to consult at any time from any device.
Sounds like there are many functionalities, does not it? And it seems like it would require several applications, but in reality, it does not! The expert does not need to have several apps to do it.
For example, ViiBE’s pre-packaged integration kit allows the implementation of such integrations in under 15 minutes.
3.3. Reduces costs associated with manual data entry
When data flows seamlessly between systems, there is no longer a need to manually enter or transfer information. It streamlines operations, reduces errors, and eliminates the need to duplicate data entry between the used applications or synchronize their systems.
3.4. Scalability
Interoperability allows companies to enhance their product suites based on their growing needs and changing requirements. New tools can be added without disrupting the operational flow and incurring substantial costs associated with data management. As a result, companies can remain agile and meet their customers’ needs in a cost-effective way.
3.5. Ecosystem development
What comes first: the chicken or the egg? In other words, is it the market that demands solutions to be interoperable or is it the solutions themselves that initiate it because they wanted to expand their market shares? The question is debatable. While different experts share different opinions, it is clear that interoperability promotes the development of new services and products.
Companies leverage APIs and create solutions that integrate with multiple platforms developing new ecosystems that are part of a big global digital market.
4. Conclusion
To sum up, interoperability is a vital component of the digital market that benefits companies and consumers. As the digital landscape evolves and companies strive to deliver value, expand their customer base, and remain adaptable in a fast-paced environment, interoperability will remain inseparable.